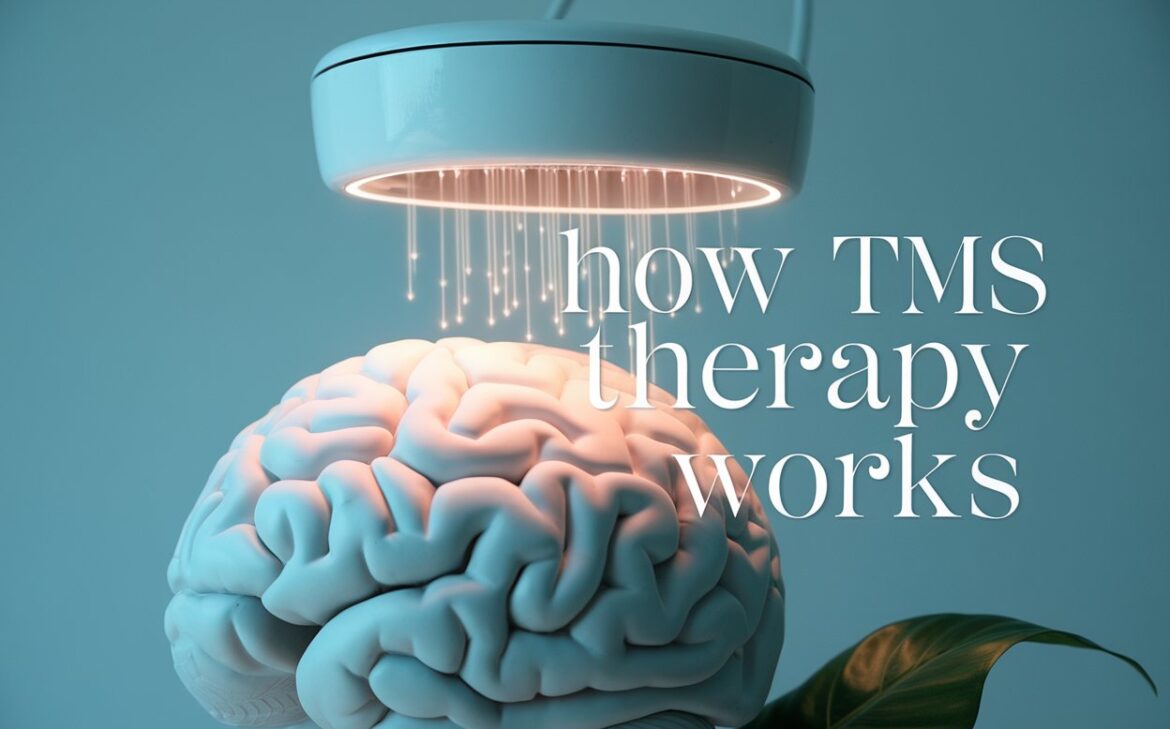
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment that helps stimulate nerve cells in the brain. You might be wondering, how transcranial magnetic stimulation works and why it has gained so much attention. TMS is especially useful for people dealing with depression who have not found success with other treatments like medication or therapy. This guide will break down how TMS therapy works in simple terms.
What is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation?
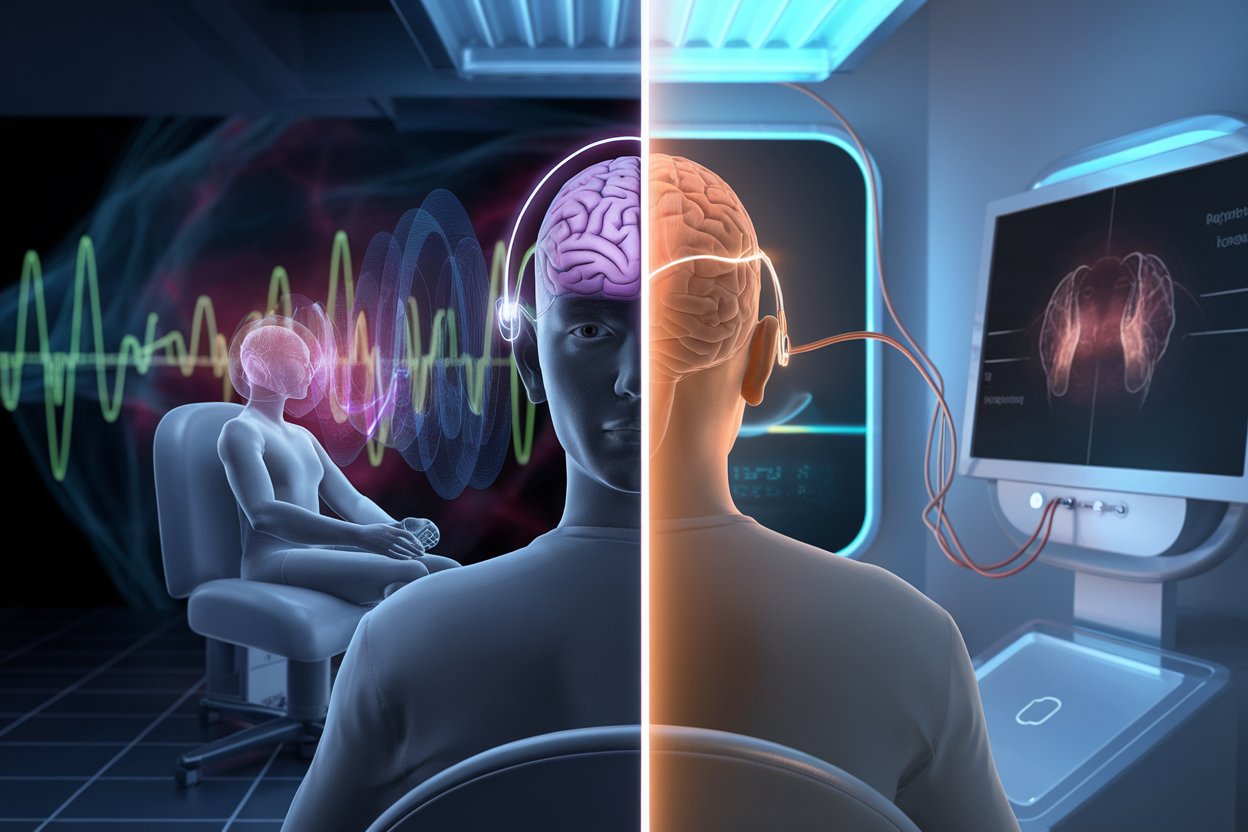
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a treatment that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate certain areas of the brain. These magnetic pulses help activate regions of the brain that may be underactive, especially in people with mental health issues like depression. TMS is also used for conditions such as anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
It’s called noninvasive because it doesn’t involve surgery or any cuts to the skin. It’s done as an outpatient procedure, which means you don’t have to stay in a hospital.
How Does Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Work?
So, how transcranial magnetic stimulation works is quite fascinating. The TMS device uses a magnetic coil placed on your head, usually above the forehead. The coil sends magnetic pulses into the brain, specifically targeting the prefrontal cortex—an area involved in mood regulation.
These pulses create small electrical currents that stimulate nerve cells in the brain. The goal is to improve the activity in the less active areas, which can help lift symptoms of depression and improve overall mood. It’s like giving your brain a little nudge to get it back on track.
What to Expect During a TMS Session
If you’re considering TMS, it helps to know what the process feels like. During a typical session, you’ll sit comfortably in a chair while a technician places a magnetic coil on your head. You don’t need anesthesia, and you’ll be awake the entire time.
You might hear a clicking sound as the machine releases the magnetic pulses. Many people feel a light tapping or knocking sensation on their head, but it’s usually not painful. Each session lasts between 30 and 60 minutes, and you can go about your daily activities right afterward.
The Science Behind TMS
The idea behind TMS is to stimulate the brain’s nerve cells to improve communication between them. But how transcranial magnetic stimulation works at a deeper level involves altering the brain’s electrical activity. People with depression often have less activity in parts of the brain that control mood. By stimulating these areas, TMS helps restore normal activity and can lead to improved mood and reduced symptoms.
TMS works through repetitive pulses, often called repetitive TMS (rTMS). These repeated pulses help make long-term changes in the brain’s activity. This process is thought to help in the release of chemicals like serotonin and dopamine, which are important for mood regulation.
Who is a Candidate for TMS?
TMS is usually recommended for individuals with depression who have not responded well to medication or therapy. It is also used for other conditions like OCD and anxiety, but it’s mainly known for treating treatment-resistant depression.
However, TMS is not for everyone. People with metal implants near their heads, such as cochlear implants or deep brain stimulation devices, should not undergo TMS. The magnetic pulses can interfere with these devices and lead to complications.
Benefits of TMS Therapy
TMS offers many benefits, especially for those who have struggled to find relief with other forms of treatment. Some of the main benefits include:
- Noninvasive: There is no surgery or anesthesia involved.
- Minimal Side Effects: Unlike medications, TMS does not cause weight gain or sexual side effects.
- Outpatient Procedure: You can continue your regular activities right after each session.
How Long Does TMS Treatment Take?
TMS is not a one-time treatment. Typically, a full course of TMS therapy involves daily sessions (five times a week) for four to six weeks. Each session lasts about 30 to 60 minutes. Most people begin to notice improvements after the first couple of weeks.
The length and frequency of the sessions are important because the brain needs repeated stimulation to create lasting changes. It’s similar to how exercising regularly helps strengthen muscles—repetition is key to improvement.
Side Effects of TMS
While TMS is considered safe, it can come with some mild side effects. The most common side effects are:
- Headache
- Scalp discomfort
- Lightheadedness
These side effects usually go away after a few sessions as your body gets used to the treatment. Serious side effects, like seizures, are extremely rare.
How Effective is TMS?
Many people wonder how effective TMS is in treating conditions like depression. Studies have shown that TMS can significantly improve symptoms in people who have not had success with antidepressants. Some even experience complete remission from their symptoms.
The success rate varies, but many people report feeling better after a full course of treatment. It’s important to note that while TMS can be very effective, it doesn’t work for everyone. If TMS is effective, your doctor may recommend maintenance sessions to keep the symptoms at bay.
Differences Between TMS and Other Treatments
One question that often comes up is how TMS compares to other brain stimulation treatments like Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). Unlike ECT, TMS does not require anesthesia and doesn’t cause memory loss. ECT involves using electrical currents to trigger a seizure, while TMS uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific areas without inducing a seizure.
Compared to medication, TMS does not have side effects like nausea, fatigue, or weight gain, which are often associated with antidepressants. This makes TMS an attractive option for those who cannot tolerate the side effects of medication.
Deep TMS vs. rTMS: What’s the Difference?
You may also hear about Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) in addition to regular TMS, known as repetitive TMS (rTMS). Both methods use magnetic pulses, but Deep TMS goes deeper into the brain, affecting a wider area. It’s often used for patients who have not responded to rTMS. The choice between these methods depends on the specific needs of the patient.
How to Prepare for a TMS Session
There isn’t much you need to do to prepare for TMS, but here are a few tips:
- Remove Metal Accessories: Take off any jewelry, hair clips, or other metal objects.
- Stay Relaxed: There’s no need to feel anxious—TMS is safe and generally well-tolerated.
- Communicate: If you feel uncomfortable during the session, let your technician know. They can make adjustments to help you.
Summary
In conclusion, how transcranial magnetic stimulation works involves using magnetic pulses to stimulate specific areas of the brain that are linked to mood regulation. This non-invasive procedure is effective for people who have not found relief from depression through other means. By improving brain activity in key areas, TMS helps restore balance and ease symptoms.
TMS is a promising option for those dealing with treatment-resistant depression. If you’re considering TMS, talk to your healthcare provider to see if it’s the right step for you. With minimal side effects, no need for surgery, and the ability to return to daily activities immediately, TMS provides a hopeful path for many people struggling with depression.
Take the First Step Towards Healing with TMS Therapy!
If you’re struggling with depression and other treatments haven’t worked, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) could be the solution you need. Discover how TMS works and its potential to transform your mental health. Schedule a consultation with our experts at American TMS Clinics today and start your journey to recovery!