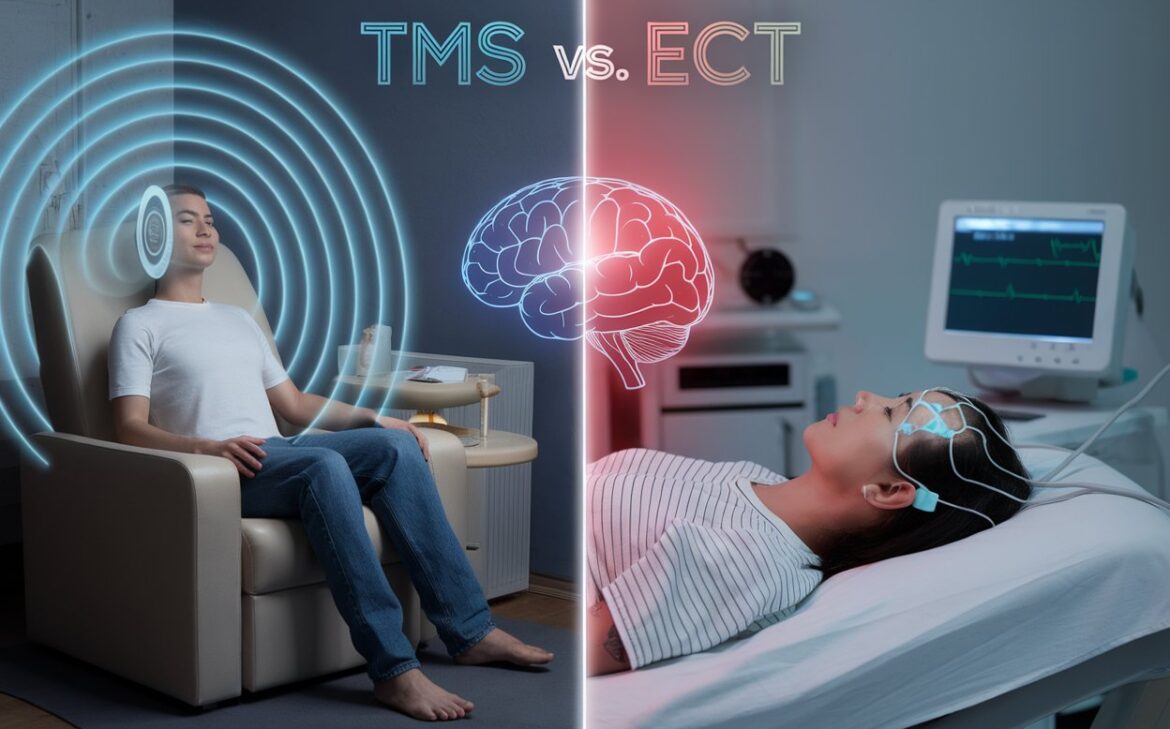
Depression affects millions worldwide, and not every patient finds relief with medication. If you’re exploring alternative treatments, TMS Therapy vs. ECT might be on your radar. These two non-pharmacological therapies target the brain but differ significantly in approach, safety, and outcomes. Understanding the key differences can help you decide which treatment is better suited to your needs.
In this guide, we’ll explore Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation vs. ECT, covering their benefits, risks, and how each affects your brain. Let me walk you into the details to determine which option might work best for you.
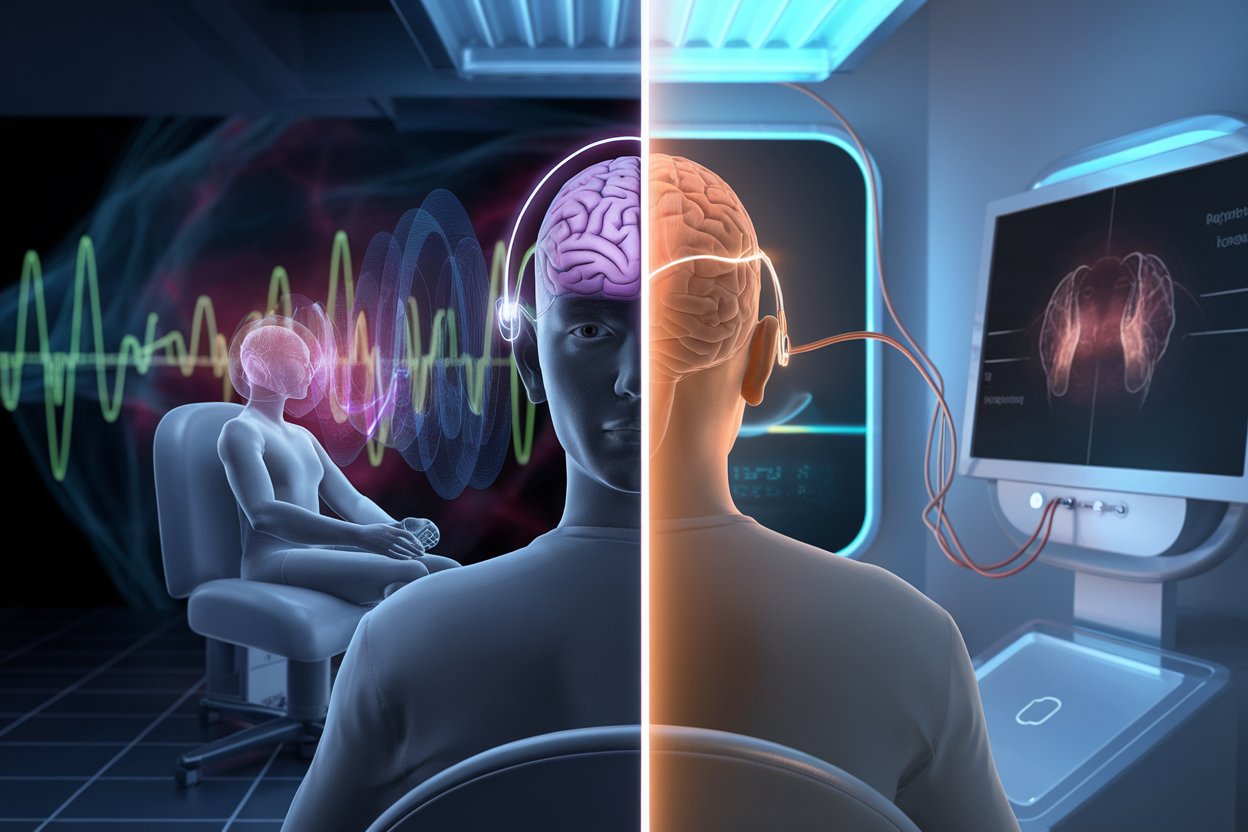
What is TMS and How Does It Work?
TMS therapy, or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is a non-invasive treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain areas associated with mood regulation. Approved by the FDA, it’s commonly used for treatment-resistant depression and other mental health conditions.
Pros and Cons of TMS Therapy
Pros:
- It is non-invasive and doesn’t require anesthesia.
- Minimal side effects, such as mild headaches or scalp discomfort.
- Allows patients to resume daily activities immediately.
- Proven effectiveness for treatment-resistant depression.
Cons:
- Requires multiple sessions (typically 20-40).
- It is not suitable for individuals with metal implants or seizure disorders.
- Insurance coverage may vary based on medical history.
TMS therapy has helped countless patients achieve significant symptom relief, offering a promising alternative for those not responding to medication.
What is ECT and How Does it Work?
ECT, or Electroconvulsive Therapy, involves delivering small electric currents to the brain to induce a controlled seizure. This process can reset brain activity, offering relief for severe depression, bipolar disorder, and other conditions. It’s typically reserved as a last-resort treatment when other options fail.
Pros and Cons of ECT
Pros:
- Highly effective for severe depression and life-threatening mental health conditions.
- Provides rapid results, often within a few sessions.
Cons:
- It is invasive and requires anesthesia.
- Common side effects include memory loss, confusion, and headaches.
- Often requires hospitalization and caregiver support.
- Negative perception due to its portrayal in popular media.
While ECT can be life-saving, it’s generally recommended for patients with severe or treatment-resistant conditions where other therapies have proven ineffective.
How Do TMS and ECT Differ in Procedure and Experience?
Treatment Sessions
- TMS Therapy vs Electric Shock (ECT): TMS sessions last about 20-40 minutes and are done while you’re awake and alert. ECT sessions are shorter but require preparation for anesthesia.
- Frequency: TMS typically requires daily sessions over 4-6 weeks. ECT might need fewer sessions but involves recovery time.
Side Effects and Recovery
- TMS Side Effects: Mild headache or scalp discomfort.
- ECT Side Effects: Potential memory loss, confusion, muscle aches.
Who Is a Good Candidate?
Deciding whether TMS Therapy vs ECT is right for you involves evaluating your medical history, the severity of your depression, and how you’ve responded to previous treatments. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can assess your condition and recommend the best treatment option. They will help you understand the benefits and risks of each treatment, ensuring you make an informed decision tailored to your needs. Here are some common criteria for TMS and ECT candidates:
TMS Candidates
- Those with moderate depression do not respond to meds.
- Individuals seeking a non-invasive treatment option.
- People without metal implants near the head.
ECT Candidates
- Patients with severe, treatment-resistant depression.
- Individuals needing rapid symptom relief.
- Those who haven’t benefited from TMS or medications.
By understanding who is a good candidate for TMS or ECT, you can work with your doctor to choose the best treatment to improve your mental health and overall well-being.
How ECT and TMS Affect Your Brain
TMS and ECT both target the brain but in different ways. TMS uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific brain areas linked to mood. ECT, on the other hand, uses electrical currents to induce a controlled seizure, effectively “resetting” certain brain pathways.
The differences in how they interact with the brain also mean that they have different side effects. TMS is generally safer with minimal impact on memory, whereas ECT can sometimes lead to temporary or even long-term memory issues
TMS Therapy vs. ECT: Which One is Better?
Choosing between TMS and ECT depends on your specific needs. TMS is less invasive with fewer side effects, making it a good first option. ECT is more powerful and works faster, ideal for severe cases. Consider your medical history, and treatment goals, and discuss them with your doctor to decide which is better for you. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | TMS Therapy | ECT |
| Procedure | Non-invasive magnetic stimulation | Induces seizures with electric currents |
| Side Effects | Mild headaches, scalp discomfort | Memory loss, confusion, headaches |
| Anesthesia | Not required | Required |
| Recovery Time | Immediate | Extended |
| Effectiveness | High for moderate to severe cases | Very high for severe cases |
For most patients, TMS is preferred due to its safety and minimal disruption to daily life. ECT, while effective, is typically reserved for emergencies or when TMS doesn’t work.
Why Choose TMS Over ECT?
There are several reasons why Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation vs. ECT may lean in favor of TMS for many patients:
- Non-Invasiveness: TMS doesn’t involve surgery or sedation, making it a convenient option.
- Fewer Side Effects: No memory loss or cognitive disruptions like those seen with ECT.
- Accessibility: TMS sessions are quick, allowing patients to maintain their routine.
- Cost-Effective: Although TMS requires more sessions, the overall cost is often lower than ECT.
TMS is a modern treatment designed for patient comfort and efficacy, making it an excellent choice for managing mental health conditions with fewer risks.
Final Thoughts
When comparing TMS Therapy vs. ECT, it’s clear that both treatments offer unique benefits for managing depression and other mental health challenges. However, TMS is often the preferred option for its non-invasive nature, minimal side effects, and ability to fit seamlessly into daily life. ECT remains a powerful tool for severe cases, but its risks and invasiveness make it a last-resort treatment.
If you’re considering either therapy, consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations. With the right information, you can choose the treatment that aligns with your needs and brings you closer to relief.
Ready to Explore a Personalized TMS Treatment Plan?
If you’re struggling with depression and looking for a non-invasive, effective alternative to medication, American TMS Clinics is here to help. Our compassionate team offers FDA-approved TMS therapy tailored to your unique needs, ensuring a safe and supportive experience throughout your journey to wellness.
Schedule a Free Consultation Today and take the first step towards better mental health.