With over 280 million people worldwide suffering from depression, finding effective treatment is a top priority. For many, the challenge lies in choosing the right option: TMS therapy vs medication. Both approaches have unique strengths and limitations, making the choice deeply personal. This article provides a detailed comparison of these two treatments to help you decide which option might work best for you.
Understanding the Basics
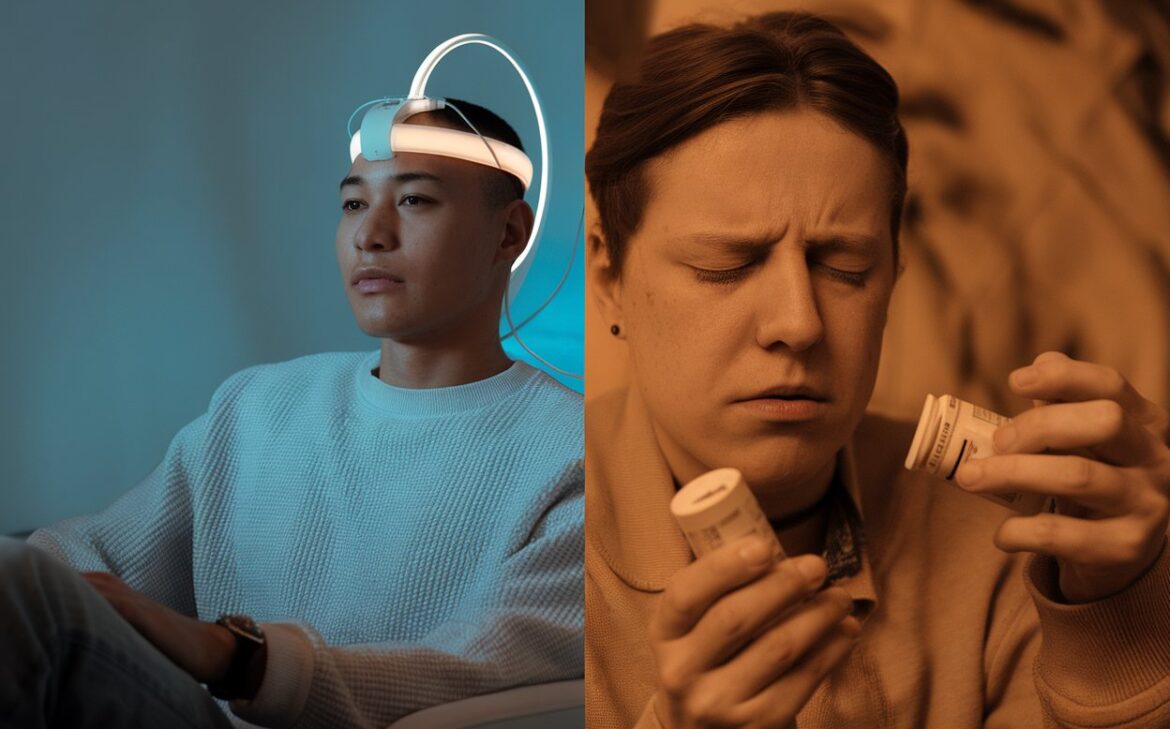
TMS Therapy is a non-invasive, drug-free depression treatment using magnetic pulses to stimulate brain activity. It’s a safe, effective option for patients with treatment-resistant depression.
What Is TMS Therapy?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. This stimulation helps regulate brain activity, particularly in areas linked to mood and depression. TMS is often recommended for patients with treatment-resistant depression, meaning traditional medications have not worked.
Unlike medication, TMS doesn’t involve systemic changes in the body. Patients undergo sessions at a clinic, typically lasting 20-40 minutes, five times a week for several weeks. The procedure is safe, with minimal side effects like mild headaches or scalp discomfort.
Key Highlights of TMS Therapy:
- Non-invasive and drug-free.
- Suitable for individuals who haven’t responded to antidepressants.
- Sessions are time-consuming but effective for many.
What Is Medication for Depression?
Antidepressant medication has been a cornerstone of depression treatment for decades. These drugs, such as Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs), work by balancing neurotransmitters in the brain. Medications are easy to take at home and often produce results within weeks.
However, they come with side effects like nausea, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction. While many people find relief with medication, some experience diminishing effects over time or struggle with long-term dependency.
Common Types of Antidepressants:
- SSRIs: Examples include Prozac and Zoloft.
- SNRIs: Medications like Effexor and Cymbalta.
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Effective but often associated with more side effects.
Why Compare Them?
The growing interest in non-pharmacological treatments like TMS stems from concerns about medication side effects, long-term use, and dependency. At the same time, antidepressants remain a widely accessible and proven option for many individuals. Comparing these treatments helps you weigh the pros and cons based on your unique needs.
Effectiveness in Treating Depression
Understanding how effective a treatment is can guide your decision. Both TMS Therapy and Spravato have demonstrated success in addressing depression, especially for those with treatment-resistant cases. Here’s how TMS performs.
Clinical Efficacy of TMS Therapy
TMS therapy has shown promising results, especially for individuals who don’t respond to medication. Studies indicate that 50-60% of people with treatment-resistant depression experience significant relief after completing TMS sessions. Approximately one-third of these individuals achieve full remission.
The time frame for improvement varies, but most patients notice changes within two to four weeks of starting treatment. TMS is particularly effective for individuals with severe depression, although its benefits for mild or moderate cases are still being explored.
Limitations:
- Requires consistent clinic visits over weeks.
- May not be effective for all forms of depression.
Clinical Efficacy of Medication
Antidepressants have a long history of success, especially for mild to moderate depression. Studies suggest that around 70% of individuals experience some improvement, though the degree varies. Medications typically take two to six weeks to show results, and achieving the right balance may require trial and error with different drugs and dosages.
However, medication efficacy can decline over time. Some patients experience “treatment fatigue,” where the effectiveness wanes, requiring dosage adjustments or new prescriptions.
Comparison of Effectiveness
When comparing TMS therapy vs medication, the differences often come down to individual needs. While TMS is ideal for treatment-resistant depression, medication remains a versatile option for most cases. Both approaches can be highly effective, but factors like patient adherence, the severity of depression, and personal preferences play a significant role.
Side Effects and Safety Profiles
Understanding the side effects and safety of any treatment is essential. This section compares the tolerability of TMS Therapy and its minimal risks, helping you make an informed choice.
TMS Therapy Side Effects
TMS is generally well-tolerated, with few side effects. Most patients report only mild headaches or scalp discomfort, which usually subside after the first few sessions. Unlike medication, TMS doesn’t cause systemic effects like nausea or weight gain.
Rare risks include seizures, but these are extremely uncommon when performed by trained professionals. TMS is also a safer option for individuals who cannot tolerate medication due to medical conditions or drug interactions.
Medication Side Effects
Antidepressants often cause more noticeable side effects, especially in the early stages. Common issues include:
- Weight gain.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Gastrointestinal problems (e.g., nausea, diarrhea).
Long-term concerns include dependency and withdrawal symptoms if the medication is stopped abruptly. Drug interactions with other prescriptions or alcohol are another drawback, particularly for individuals managing multiple health conditions.
Safety Comparison
TMS’s localized impact makes it a safer choice for individuals concerned about systemic side effects. However, medication is a more straightforward option for those without significant health risks or sensitivities. For pregnant individuals, the elderly, or those with complex medical histories, TMS may be preferable.
Accessibility, Cost, and Convenience
When considering treatment options like TMS Therapy, practical factors like time, affordability, and ease of access play a crucial role. Let’s examine how these impact patients’ choices.
TMS Therapy
While effective, TMS therapy requires a significant time commitment. Patients need to visit a clinic several times a week for up to six weeks. The cost can be high—typically $300-$500 per session—but many insurance plans cover it for treatment-resistant depression.
Medication
Antidepressants are widely accessible and cost-effective, especially with generic options. They don’t require frequent doctor visits beyond initial prescriptions and follow-ups. However, the long-term cost of medications can add up, particularly if multiple adjustments are needed.
Comparison
In terms of convenience, medication is often the easier choice. However, for individuals seeking an alternative to daily pills, TMS offers a compelling option, provided they can manage the time and financial investment.
Patient Experiences and Preferences
Understanding real patient experiences can provide valuable insight into treatment options. Here, we explore how individuals perceive TMS Therapy, shedding light on its impact and transformative potential.
TMS Therapy Testimonials
Patients often describe TMS as life-changing, particularly those who’ve struggled with medication. They report feeling “clear-headed” and more focused, without the fog of side effects. Testimonials highlight the relief it brings after years of frustration with traditional treatments.
Medication User Experiences
Medication reviews vary widely. Some individuals find antidepressants to be a simple, effective solution, while others struggle with side effects or the need for constant adjustments. Success often hinges on finding the right drug and dosage—a process that can take months.
Emotional and Psychological Factors
Choosing between TMS and medication also involves emotional considerations. For some, the stigma of undergoing brain stimulation may deter them, while others may dislike the idea of long-term chemical dependency. Personal comfort and confidence in the chosen treatment are crucial.
Conclusion
The choice between TMS therapy and medication isn’t straightforward. Both options offer unique benefits and limitations. TMS is ideal for individuals who have not found relief with medication and prefer a non-invasive approach. Medication, on the other hand, remains a proven, accessible treatment for many forms of depression.
Ultimately, the “better” option depends on individual needs, severity of symptoms, and personal preferences. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to create a tailored treatment plan. With the right guidance, you can find the relief you deserve.
Take Control with TMS Therapy – Learn More Today!
Ready to explore effective, drug-free depression treatment? Visit American TMS Clinics today to learn how TMS therapy can help you regain control.